
Linux 文件系统架构从 VFS 到数据存储
Linux 系统的文件管理是其操作系统架构中的核心组成部分,涉及到从虚拟文件系统(VFS)到物理磁盘的整个过程。理解这一过程对于系统管理员、开发人员甚至普通用户来说,都具有重要意义。通过掌握 Linux 文件系统架构,我们可以更加高效地进行...

Linux PS命令优化香港服务器进程管理
Linux系统作为全球最流行的服务器操作系统之一,在服务器管理中扮演着不可或缺的角色。对于Linux服务器的管理员来说,了解和熟练使用一些基本的命令工具,尤其是像PS命令(Process Status命令),将大大提升服务器的管理效率。PS...

如何启用Windows Sandbox以提升香港服务器安全性
随着网络安全威胁不断升级,越来越多的企业和个人开始关注如何保护自己的计算机系统免受各种潜在的攻击和恶意软件侵害。在这方面,Windows Sandbox成为了一个非常有效的工具,特别是对于那些使用Windows操作系统的用户来说。Windo...

niihost香港BGP服务器高性能、稳定性与低延迟
NiiHost香港BGP服务器是一种面向全球用户,尤其是希望实现中国大陆访问优化的优质云主机解决方案。它将香港作为节点,与多个国际运营商和网络交换中心建立连接,通过BGP多线路技术实现网络高可用性与多样化路径选择,从而在满足高稳定性、高带宽...

TW-HINET三网回程优化
TW-HINET是NiiHost 推出的一系列针对台湾 HiNet(中华电信骨干网络)进行三网回程优化的 VPS 服务。它结合了 NAT 与 VDS(虚拟专用服务器)两类方案,为用户提供高性能、低延迟、灵活计费且成本优越的主机选择。无论你是...
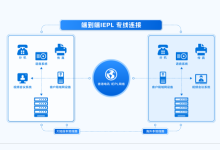
专线IEPL高速网络
专线IEPL高速网络一直被视为跨境业务中最核心的基础设施,它不仅决定着企业通信的质量,也直接影响跨境业务的效率、访问体验、数据同步速度、远程协作质量以及平台运营稳定性。随着跨境行业不断增长,越来越多用户发现传统公网线路无法提供足够稳定的连接...
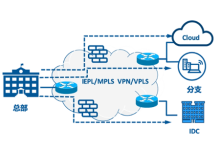
IEPL专线广港加强高速网络
IEPL专线作为跨境网络和全球互联场景中最具代表性的高质量专线产品,一直被视为中小企业、跨境电商、内容团队、直播业务、远程办公团队,以及需要稳定回国链路与国际出口链路的用户不可或缺的基础设施。它的核心价值,不只是解决“能不能连”的问题,而是...

4家香港服务器推荐看这篇就够了
在选择香港服务器服务时,用户往往会考虑网络延迟、带宽质量、稳定性、计费方式等多个因素。下面介绍四家值得关注的主机商:Back Waves (GlobalShare)、BageVM(香港 Lite)、NiiHost(香港 Dedicated)...

SSH远程连接超时断开常见解决方法
SSH(Secure Shell)几乎是每位系统管理员和开发者每天都会使用的工具。它为Linux、Unix以及各种网络设备提供了安全、可靠的远程管理方式。然而,在使用过程中,许多人会遇到 SSH远程连接超时断开 的问题,这不仅影响工作效率,...

Windows防火墙开启与禁用Ping的详细讲解
Ping(ICMP回显请求)是判断网络连通性和排查故障的重要工具。然而,出于安全性考虑,许多企业和个人用户可能希望禁用Ping,以防止外部网络扫描和潜在攻击。本文将详细介绍如何在Windows系统中配置防火墙以开启或禁用Ping功能,帮助美...
- 1
- 2
- 共 2 页

 全球服务器测评
全球服务器测评